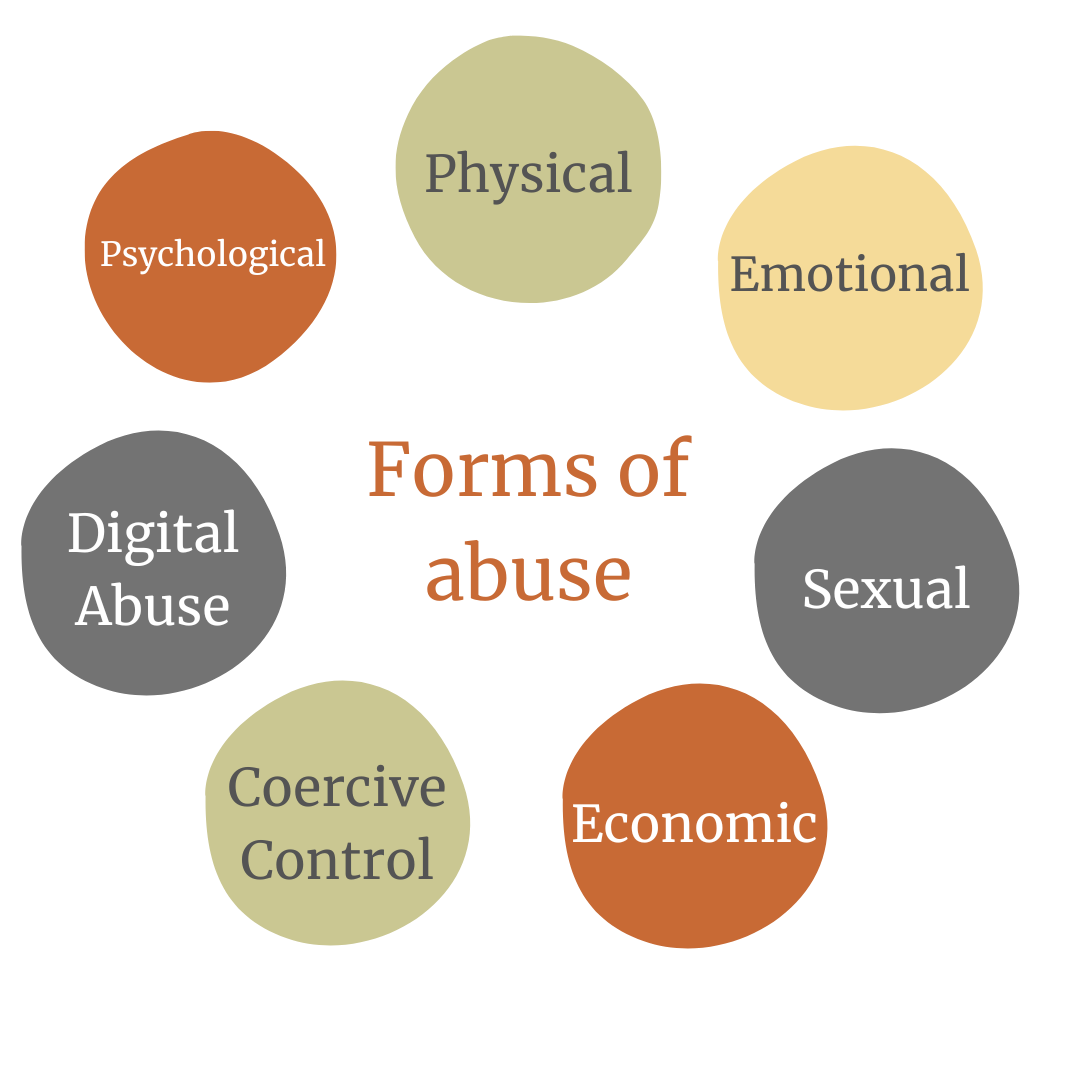
What is domestic Abuse?
Domestic Abuse isn’t just physical abuse. Domestic abuse includes physical, emotional, sexual, financial and economic, coercive control, digital and psychological abuse.
Domestic abuse is an incident or pattern of incidents of controlling, bullying, threatening or violent behaviour, by a partner, ex partner or family member.
Abusive behaviour can happen in any relationship and it can continue even after the relationship has ended.
Physical abuse is any violence or intentional and unwanted contact with your body.
Some examples of physical abuse are:
Scratching, punching, biting, strangling or kicking.
Throwing something at you such as a phone, book, shoe or plate.
Pulling your hair.
Pushing or pulling you.
Grabbing your clothing.
Grabbing you to prevent you from leaving or to force you to go somewhere.
Emotional abuse includes threats, insults, humiliation, intimidation, isolation or stalking.
Some examples of emotional abuse are:
Calling you names and putting you down.
Yelling and screaming at you.
Intentionally embarrassing you in public.
Preventing you from seeing or talking with friends and family.
Telling you what to do and wear.
Damaging your property when they’re angry (throwing objects, punching walls, kicking doors, etc.)
Blaming your actions for their abusive or unhealthy behaviour.
Threatening to commit suicide to keep you from breaking up with them.
Threatening to harm you, your pet or people you care about.
Making you feel guilty or immature when you don’t consent to sexual activity.
Threatening to have your children taken away
Sexual abuse refers to any action that pressures you to do something sexually you don’t want to do.
Some examples of sexual abuse are:
Unwanted kissing or touching.
Unwanted rough or violent sexual activity.
Rape or attempted rape.
Refusing to use condoms or restricting your access to birth control.
Threatening you into unwanted sexual activity.
Pressuring or forcing you to have sex or perform sexual acts.
Using sexual insults toward you.
Economic abuse can be very subtle — telling you what you can and cannot buy or requiring you to share control of your bank accounts.
Some examples of economic abuse are:
Giving you an allowance and closely watching what you buy.
Placing your wages in their account and denying you access to it.
Keeping you from seeing shared bank accounts or records.
Forbidding you to work or limiting the hours you do.
Preventing you from going to work i.e. by taking your car or keys.
Getting you fired by harassing you, your employer or coworkers on the job.
Maxing out your credit cards without your permission.
Refusing to give you money for food, rent, medicine or clothing.
Spending money on themselves but not allowing you to do the same.
A pattern of intimidation, degradation, isolation and control with the use or threat of physical or sexual violence.
Some examples of coercive control are:
Unreasonable demands.
Degradation.
Restricting daily activities.
Threats or intimidation.
Financial control.
Monitoring of time.
Taking your phone away.
Deprivation of food.
Destruction of possessions.
The use of technologies such as texting and social networking to bully, harass, stalk or intimidate a partner. Often this behaviour is a form of verbal or emotional abuse perpetrated online.
Some examples of digital abuse are when someone:
Tells you who you can or can’t be friends with on Facebook and other sites.
Sends you negative, insulting or threatening emails, Facebook messages, Xeets (formerly known as tweets), direct messages or other messages online.
Uses sites like Facebook, X (formerly known as Twitter), Instagram and others to keep constant tabs on you.
Posts negative things about you.
Sends you unwanted, explicit pictures and/or demands you send some in return.
Pressures you to send explicit video or sexts.
Steals or insists to be given your passwords.
Constantly texts you and makes you feel like you can’t be separated from your phone for fear that you will be punished.
Looks through your phone frequently, checks up on your pictures, texts and outgoing calls.
Tags you unkindly in pictures on Instagram, Tumblr, etc.
A person subjecting another person to behaviour which may result in psychological trauma including anxiety, chronic depression or post-traumatic stress disorder.
Some examples of psychological abuse are:
Gaslighting – manipulating you into doubting your own sanity or reality.
Moving things around the house, or removing them and returning them later, then denying it.
Denying that you or they said things.
Telling you that people have said things about you, or that your friends don’t like you.
Telling you that you have a mental health condition when you haven’t.
Making derogatory jokes about you to others in front of you.
Name calling, telling you you are useless, stupid, worthless and mad.
Questioning you endlessly about everything you do or say.